Ferrite Magnets
Ferrite magnets are resistant to many chemical substances, such as solvents, bleaches and fluorhydric acid. Ferrite magnets are quality, economical components that can be found in applications as diverse as automation, control, measurement and others. Ferrite magnets can be isotropic or anisotropic: for anisotropic qualities, the particles are aligned in a single direction, obtaining better magnetic characteristics.
-
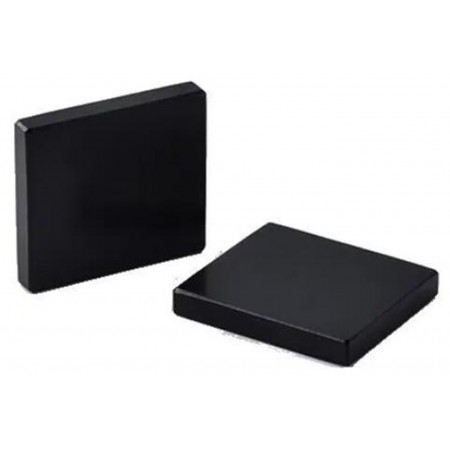
Ferrite Blocks
 Ferrite blocks are composite materials used in the manufacture of transformer cores and inductor coils. Ferrite is a ceramic material that has unique magnetic properties that make it ideal for use in high frequency applications.
Ferrite blocks are composite materials used in the manufacture of transformer cores and inductor coils. Ferrite is a ceramic material that has unique magnetic properties that make it ideal for use in high frequency applications.Ferrite is a ferromagnetic material composed mainly of iron oxide (Fe3O4) and zinc oxide (ZnO). Ferrite blocks are made from a mixture of ferrite powder and a binding agent, which is molded and fired at a high temperature to form a solid block.
Ferrite blocks are commonly used in the construction of transformer cores and inductor coils due to their unique magnetic properties. Ferrite has a very high magnetic permeability at frequencies up to several megahertz, which means that it can concentrate the magnetic field in a small area and increase the efficiency of the transformer or inductor.
In addition, ferrite has a very low hysteresis energy loss and high electrical resistivity, making it ideal for use in high-frequency applications. Ferrite blocks are also resistant to oxidation and corrosion, making them suitable for use in aggressive environments.
-
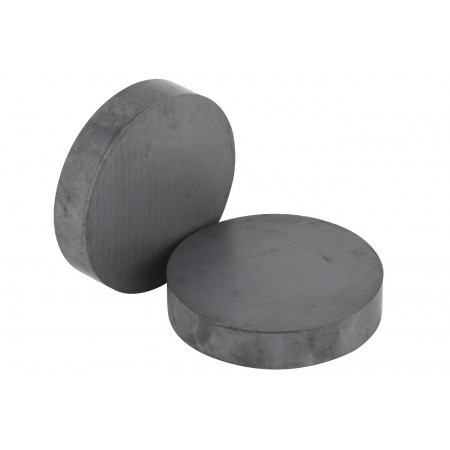
Ferrite Disks
 Ferrite discs are magnetic materials commonly used as cores in transformers and high-frequency inductor coils. They are made of ferrite, a ceramic material composed mainly of iron oxide and zinc oxide.
Ferrite discs are magnetic materials commonly used as cores in transformers and high-frequency inductor coils. They are made of ferrite, a ceramic material composed mainly of iron oxide and zinc oxide.Ferrite discs have a flat, circular structure and are manufactured in a variety of sizes and shapes to suit the specific needs of each application. They are designed to be placed inside a transformer or inductor coil to increase the efficiency and current handling capacity of the coil.
Ferrite has high magnetic permeability at high frequencies, which means that it can concentrate the magnetic field in a small area and improve the efficiency of the coil. Additionally, ferrite discs have high electrical resistance and low hysteresis loss, making them ideal for use in high-frequency applications.
Another advantage of ferrite discs is their resistance to oxidation and corrosion, making them suitable for use in harsh environments. In addition, they are relatively inexpensive and easy to manufacture in large quantities.
-
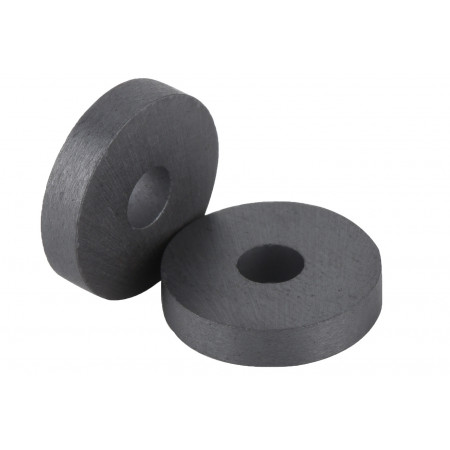
Ferrite Rings
 Ferrite rings are ferrite cores that are shaped like a ring. These components are commonly used in the manufacture of high-frequency inductors and transformers, as well as other electronic devices.
Ferrite rings are ferrite cores that are shaped like a ring. These components are commonly used in the manufacture of high-frequency inductors and transformers, as well as other electronic devices.Ferrite rings are made of ceramic material composed of iron oxide and zinc oxide. Their ring shape allows them to be wrapped around the coil leads, increasing the efficiency of the inductor or transformer.
Ferrite has a very high magnetic permeability at high frequencies, which allows the ferrite rings to focus the magnetic field and increase the efficiency of the device. In addition, ferrite has a very low hysteresis energy loss and high electrical resistivity, making it ideal for use in high-frequency applications.
Ferrite rings are also resistant to oxidation and corrosion, making them suitable for use in harsh environments. Also, they are easy to install and can be stacked to increase inductance.
-
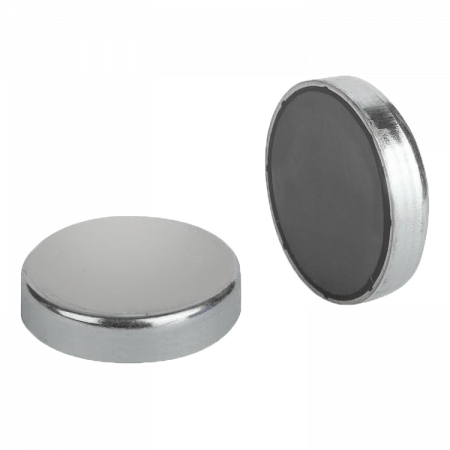
Ferrite Base
 A ferrite base is a component used in electromagnetic interference (EMI) absorbing applications. The ferrite base is made of a ceramic material composed primarily of iron oxide and zinc oxide that has unique magnetic properties that make it ideal for use in high frequency applications.
A ferrite base is a component used in electromagnetic interference (EMI) absorbing applications. The ferrite base is made of a ceramic material composed primarily of iron oxide and zinc oxide that has unique magnetic properties that make it ideal for use in high frequency applications.The ferrite base is placed in the path of electromagnetic interference and acts as a filter to absorb unwanted electromagnetic waves. By absorbing these waves, the ferrite base helps prevent electromagnetic interference that can affect the performance of sensitive electronic devices.
The ferrite base is commonly used in the manufacture of cables and connectors for electronic devices. It can be placed on the cable or connector to reduce electromagnetic interference that may be generated by other nearby electronic devices.
-
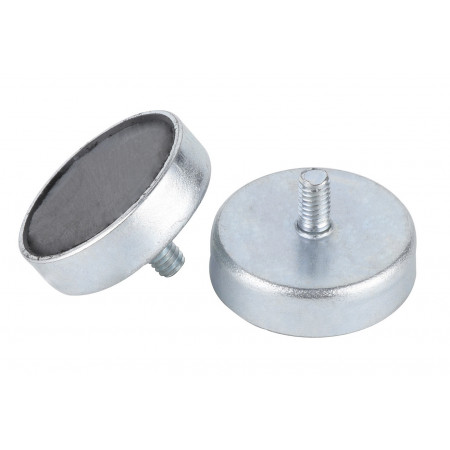
base with internal thread
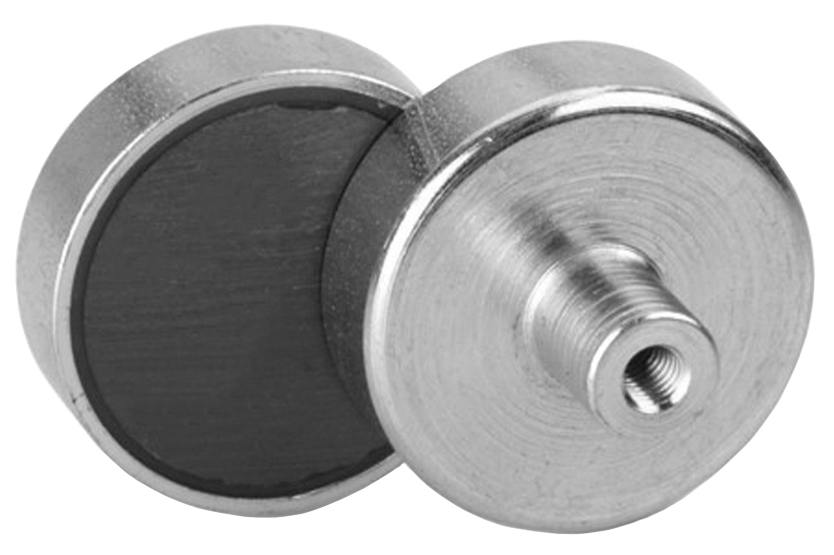 An internally threaded ferrite pad is a specific type of ferrite pad that is designed to be screwed or threaded onto an electronic component, thereby providing protection against electromagnetic interference (EMI). These sockets are commonly used in the manufacture of cables and connectors for electronic devices, and are particularly useful for applications where it is necessary to adjust the position of the ferrite socket to optimize interference absorption.
An internally threaded ferrite pad is a specific type of ferrite pad that is designed to be screwed or threaded onto an electronic component, thereby providing protection against electromagnetic interference (EMI). These sockets are commonly used in the manufacture of cables and connectors for electronic devices, and are particularly useful for applications where it is necessary to adjust the position of the ferrite socket to optimize interference absorption.The Internally Threaded Ferrite Base has a thread on the bottom, allowing it to be screwed into a threaded hole in an electronic component. Once screwed in, the ferrite base can provide effective protection against electromagnetic interference that can affect the performance of sensitive electronic devices.
As with other ferrite bases, the internally threaded ferrite base is made of a ceramic material composed primarily of iron oxide and zinc oxide that has unique magnetic properties that make it ideal for use in high frequency applications. The internally threaded ferrite base is resistant to oxidation and corrosion, making it suitable for use in harsh environments.
-
Base with External Thread
 Uma base de ferrite com rosca externa é um tipo de base projetada para ser aparafusada em um cabo ou conector, fornecendo proteção contra interferência eletromagnética (EMI). Essas bases são comumente utilizadas na fabricação de cabos e conectores para dispositivos eletrônicos, sendo particularmente úteis em aplicações onde é necessária uma proteção eficaz contra EMI.
Uma base de ferrite com rosca externa é um tipo de base projetada para ser aparafusada em um cabo ou conector, fornecendo proteção contra interferência eletromagnética (EMI). Essas bases são comumente utilizadas na fabricação de cabos e conectores para dispositivos eletrônicos, sendo particularmente úteis em aplicações onde é necessária uma proteção eficaz contra EMI.A Base de Ferrite com Rosca Externa possui uma rosca externa, permitindo que seja parafusada em um cabo ou conector. Uma vez aparafusada, a base de ferrite pode fornecer proteção eficaz contra interferência eletromagnética que pode afetar o desempenho de dispositivos eletrônicos sensíveis.
-
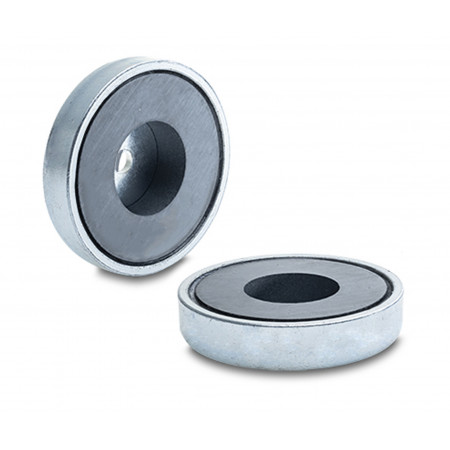
Base with Through Hole
 A through-hole ferrite base is a type of base that has a hole or hole that allows a wire or electronic component to be passed through it. These sockets are commonly used in the manufacture of cables and connectors for electronic devices, and are especially useful in applications where effective protection against electromagnetic interference (EMI) is required.
A through-hole ferrite base is a type of base that has a hole or hole that allows a wire or electronic component to be passed through it. These sockets are commonly used in the manufacture of cables and connectors for electronic devices, and are especially useful in applications where effective protection against electromagnetic interference (EMI) is required.The through hole ferrite base is made of a ceramic material composed primarily of iron oxide and zinc oxide that has unique magnetic properties making it ideal for use in high frequency applications. The hole in the ferrite base allows a cable or electronic component to pass through it, while the ferrite base provides effective protection against electromagnetic interference that can affect the performance of sensitive electronic devices.
The through hole ferrite base can have different sizes of holes to accommodate different sizes of wires or electronic components. As with other ferrite bases, the through hole ferrite base is resistant to oxidation and corrosion, making it suitable for use in harsh environments.
-
Base with Countersunk Hole
 Countersunk through-hole ferrite bases are electromagnetic components that are used in the electronics industry as suppressors of electromagnetic interference in integrated circuits, coils, transformers, among others.
Countersunk through-hole ferrite bases are electromagnetic components that are used in the electronics industry as suppressors of electromagnetic interference in integrated circuits, coils, transformers, among others.These ferrite pads are made of a ferromagnetic ceramic material that has magnetic properties that allow it to absorb and filter electromagnetic noise that can affect circuit performance and quality.
Countersunk through hole refers to the shape of the central hole of the ferrite base which has a conical shape, allowing better cable coupling inside the base.
Countersunk through hole ferrite bases are used for high frequency applications and are available in different sizes and impedance values to suit the needs of each project.
-
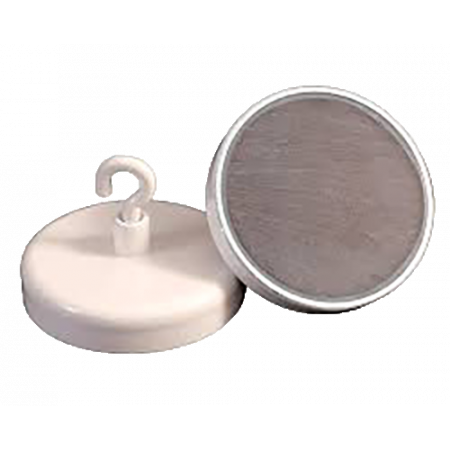
Ferrite Hooks
 Hook-shaped ferrite magnets are magnetic devices commonly used in industrial and commercial applications for holding objects, organizing cables, and other similar purposes. These magnets are made of ferrite, a ceramic material composed primarily of iron oxide and zinc oxide.
Hook-shaped ferrite magnets are magnetic devices commonly used in industrial and commercial applications for holding objects, organizing cables, and other similar purposes. These magnets are made of ferrite, a ceramic material composed primarily of iron oxide and zinc oxide.The hook shape of ferrite magnets allows them to be used in a variety of situations where a secure and stable hold is required. For example, they can be used to hold metal parts to a surface, to keep cables and pipes in place, or to organize tools and equipment in a workshop or garage.
Hook-shaped ferrite magnets are relatively strong and can withstand significant loads compared to their size. However, its magnetic strength is significantly lower than that of neodymium magnets or other more advanced magnetic materials.
Hook-shaped ferrite magnets are available in a variety of sizes and shapes, making them suitable for a wide range of applications. They are also relatively inexpensive compared to other magnet types, making them attractive for low-cost applications.
-
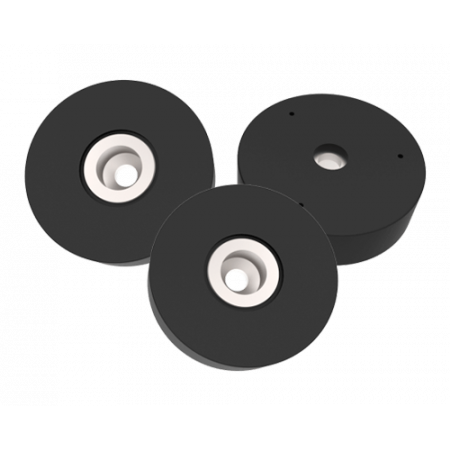
Rubber Coated Ferrite Base
 A rubber coated ferrite base is a component used in electromagnetic interference (EMI) absorbing applications. The ferrite base is a ceramic material composed primarily of iron oxide and zinc oxide that has unique magnetic properties that make it ideal for use in high frequency applications.
A rubber coated ferrite base is a component used in electromagnetic interference (EMI) absorbing applications. The ferrite base is a ceramic material composed primarily of iron oxide and zinc oxide that has unique magnetic properties that make it ideal for use in high frequency applications.The ferrite base is covered with a layer of rubber to protect it from shock and abrasion. The rubber coating also provides a smooth, non-slip surface that can be easily adhered to the surface of a case or chassis.
The rubber coated ferrite base is used to absorb electromagnetic interference that can affect the performance of sensitive electronic devices. The ferrite base is placed in the path of interference and acts as a filter to absorb unwanted electromagnetic waves.
The rubber coating protects the ferrite base from damage caused by shock and vibration, making it ideal for use in mobile devices. In addition, the rubber coated ferrite base is resistant to oxidation and corrosion, making it suitable for use in harsh environments.